What is Skewing of Rotor Slots?
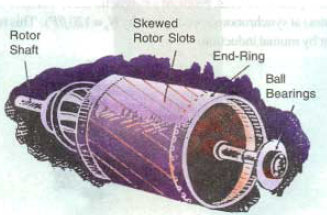
As shown in the above picture, the rotor bars of an induction motor are not parallel with the shaft, and the bars are skewed. The rotor bars are skewed purposefully to gain the following performance advantages.
Advantages of Skewing of Rotor of Induction Motor
There are the following advantages of skewing rotor slots.
- Increased Starting Torque
- Prevents Cogging
- Prevents Crawling
- Reduce Magnetic Hum
Now, we will discuss all the above points to understand the importance of the skewing of the rotor.
Increased Starting Torque:
The induction motor’s torque is proportional to the product of the rotor current and the rotor power factor. The length of the rotor bars increases with skewing.

The length of the rotor conductor is greater if the conductor is put in the skewed rotor slots. The resistance of the conductor depends on the length and the cross-sectional area of the conductor. With skewing, the rotor conductor length increases, and the cross-sectional area gets reduced.
Resistance(R)=p*L/A
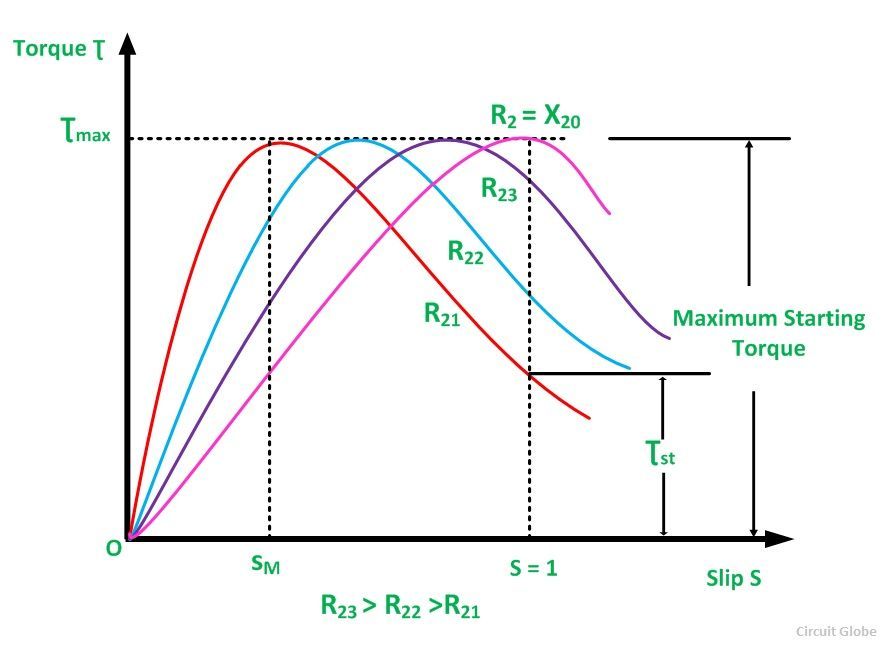
The increased resistance improves the power factor of the rotor circuit and the motor’s starting torque-delivering capacity. The higher the rotor resistance(R2), the higher the starting torque.
The speed-torque curve of the induction motor is given below.
Prevents Cogging:
If the number of stator slots is equal to the rotor slots or equal to the integral multiples of the rotor slots, and if the rotor slots are parallel to the stator slots, the motor may refuse to start because of the magnetic locking between the rotor and stator teeth. The phenomenon is called cogging.
If the rotor and the stator conductors are parallel to each other, there is a strong possibility of magnetic locking between the rotor and the stator. Therefore, the rotor slots are skewed.
Prevents Crawling:
The Phenomenon of running the induction motor at a very low speed is known as crawling. The harmonics are responsible for the crawling phenomenon. The motor may crawl at the Ns/7 or Ns/13 the speed. The skewing of the rotor reduces the tooth harmonics and thus prevents the crawling effect.
Reduces Magnetic Hum:
The skewing helps in reducing the magnetic hum, and the motor runs quieter.
Skewing Angle in Induction Motor:
The rotor skew angle formula is given below.
= 720/n(P/2) Degree electrical
Where,
P= Number of poles
n= Order of Harmonics
most usefull