Shell type transformer winding is positioned on the middle limb of the core and other limbs are used for mechanical support.The transformer can be categorized into core type transformer and shell type transformer depending on the construction of the magnetic core and arrangement of the winding of the transformer.
Table of contents
Shell Type Transformer Construction
Main Parts of the Transformer
Core
The core of the shell-type transformer is made from the E-I- and E-E-type laminated sheets.
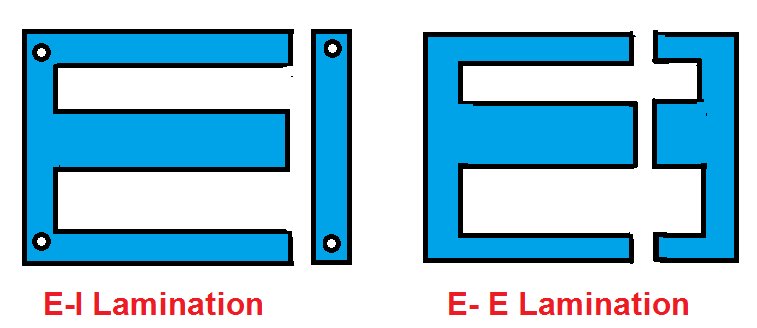
Lamination
The core of the single-phase transformer has three limbs. This arrangement increases the mechanical strength of the core. In addition to this, the winding remains protected from mechanical shock.
Winding
The HV and LV winding is wound around the central limb. The central limb carries the entire flux (Ф ). The flux (Ф ) divides into two equal parts, and thus, each side limb carries half (Ф/2 ) of the total flux(Ф ). As a result, the cross-section area of the central limb is two times the side limb area. The arrangement of the winding around the central limb is given below.
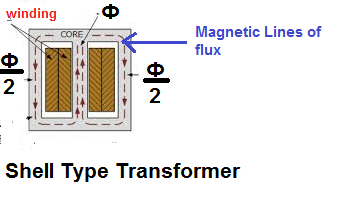
The magnetic flux flows through two closed magnetic paths, reducing the iron core losses and improving the efficiency of the transformer. This transformer gives more output than a similar core-type transformer.
The core of the transformer has good mechanical strength. The electromagnetic force developed during charging and short circuit condition cause less adverse effect on winding.
The HV and the LV winding fixes around the central limb in the sandwich arrangement. The HV winding is in between the two LV winding.
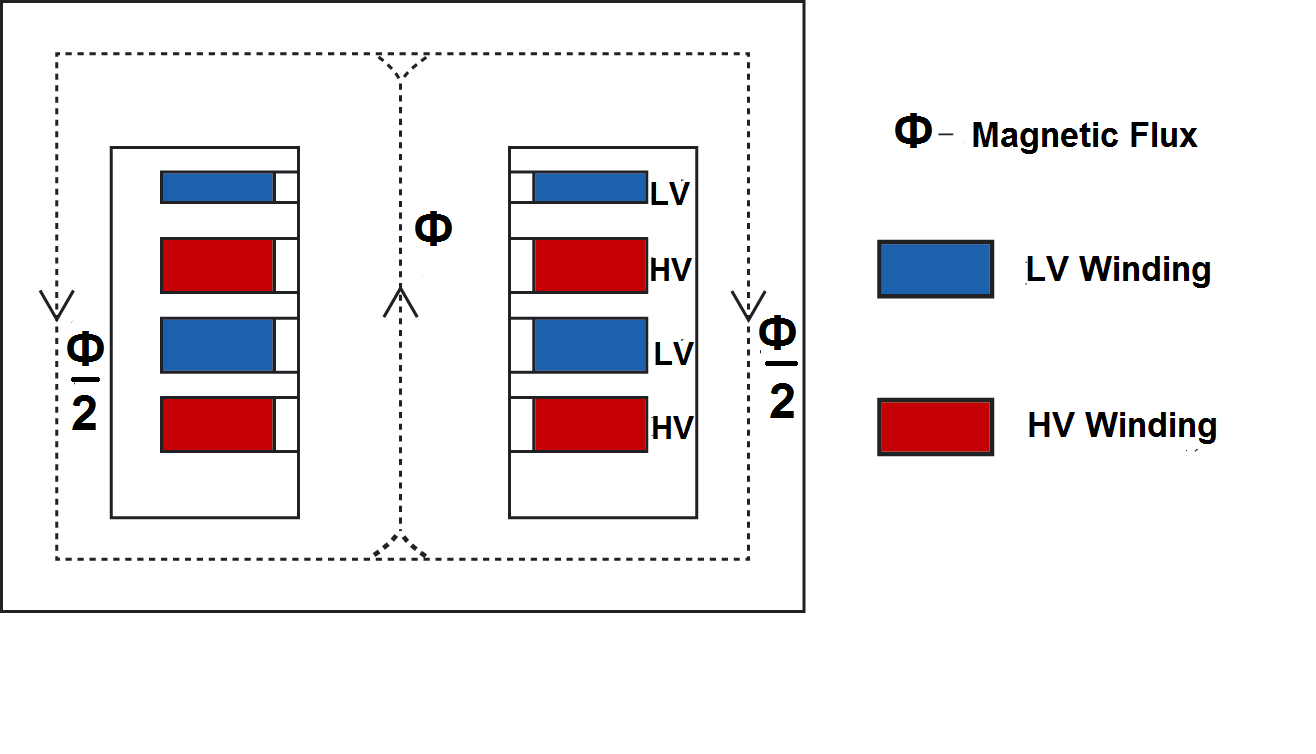
The amount of conductor required for the shell-type transformer is less because both windings are located on the central limb. However, the insulation requirement is higher than that of the core-type transformer.
This is because HV and LV windings are fixed alternatively on the same limb. The design of the transformer is complex as compared to the core-type transformer.
In case of any defect in the inner winding, the outer winding removal is a must.
Cooling System
In the case of a type transformer, natural air cooling may be sufficient. However, we need forced air or forced oil cooling for a shell-type transformer. The reason is that the yoke and limbs surround the core.
Working of Shell Type Transformer
Two coils are mounted in the central leg. First, one winding is wound, and above it, one more winding is wound. This arrangement ensures no flux leakage. On excitation of the primary winding, it generates flux & voltage is induced in the secondary winding. The working principle of shell-type and core-type transformers is based on Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction.
Read More: Core Type Transformer- Its working & Application
Applications of Shell Type Transformer
The transformer is most suitable for low-voltage applications. We use shell-type transformers for low-voltage electronic circuits. The cost of the transformer is lower because we can use the square or rectangular cross-section area core.
Merits and Demerits of Shell Type Transformer
Advantages
- Good mechanical strength
- Compact size
- Low leakage magnetic flux
- It has a high seismic-withstand ability
Disadvantages
- Needs special fabrication facilities for transformer designing
- More Iron in the core
- Complex in design
- Manufacturing cost high
- Force cooling required
- Repairing needs the removal of all the outer winding.
1 thought on “Shell Type Transformer- Construction, Working & Applications”