Semiconductor fuses are used for short circuit protection of semiconductor devices like Silicon Control rectifiers (SCRs), Insulated Gate Bipolar Devices(IGBTs), diodes, triacs, thyristors, and similar solid-state power devices. These power devices are widely used in rectifier converters, inverters, UPS systems, DC drives, Variable frequency drives, slip power recovery systems (SPRS), and a wide range of electronic equipment. The semiconductor fuse is a high rupturing capacity(HRC) fuse. Semiconductor fuse has super fast-acting characteristics specially developed to protect semiconductor power devices.
For the protection of semiconductor devices, the thermal energy (I2t) of the semiconductor fuse is selected less than the thermal energy (I2t) of the power device.
There is no semiconductor material used for constructing a fuse; the special category of the HRC fuse used for the protection of semiconductor devices is called a semiconductor fuse.
Why are fast-acting semiconductor fuses required for the protection of semiconductor devices?
The heavy current passing through the device during a short circuit fault also raises the junction temperature. If the junction temperature of the semiconductor devices increases above its rated capacity, the device is prone to fail.
If the current flowing through the semiconductor devices is more than the rated current of the device, it can lead to a rise in device temperature. If the short circuit current passes through the semiconductor device, the device is apt to fail if the fault current is not immediately interrupted by blowing off the fuse.
The resistance of the semiconductor devices gets halved with every rise in 10-degree- centigrade temperature. Thus, the temperature rise caused by overloading or over-current during fault conditions can permanently damage the semiconductor device.
The semiconductor devices are prone to failure with the rise of device temperature caused by short circuits or overcurrent through the device; therefore, a fast-acting fuse must be installed for device protection.
Semiconductor fuses are widely used in power electronics applications like thyristor DC drives, Variable frequency drives, Uninterrupted Power Supplies (UPS), Rectifiers, etc.
Semiconductor Fuse Construction:
A semiconductor fuse is a high rupturing capacity (HRC) fuse. The HRC fuse has a fuse element surrounded by a filler and enclosed by a fuse body.
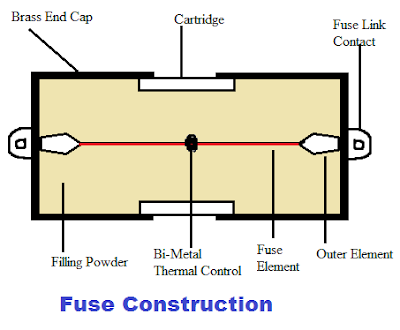
The current passes through the fuse element, producing heat according to the element resistance. The heat generated in the fuse element is passed to the filler and transferred to the fuse body. Filler material like sand and quartz provides excellent heat transfer, and thus, the lower cross-section area fuse element can be used. The small area of the fuse element makes the fuse melt under short-circuit conditions. The filler also absorbs the arc energy when the fuse clears the fault.
Semiconductor Fuse Characteristics
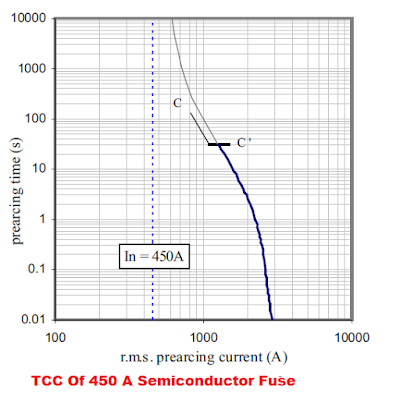
The fuse has an inverse time-current characteristic. The greater the over-current, the lesser the fault-clearing time. The semiconductor fuse exhibits super-fast fault-clearing characteristics. The metal fuse characteristics are set in line with the thermal load-carrying capacity of the semiconductor. The prearcing time of the semiconductor fuse is very short. The cut-off characteristics of the fuse are given below.
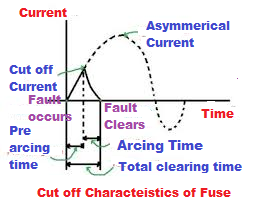
The semiconductor devices have low thermal reserves and function reliably if the junction temperature is below 125°C. The semiconductor devices have a very low temperature limit margin between the operating and the limit temperature, and super-fast-acting fuses are required to protect the semiconductor devices. The semiconductor fuse has small limiter cross-sections, and temperature is reached quickly when overcurrents are present.
The fuse element of the semiconductor fuse is made of oxidant-resistant fine silver, with regions of reduced cross-section area called ( often called notches). The silver has a melting point of 960°C, which can withstand the high operating temperature of the limiter. The fuse body is made of thermally stable aluminum oxide ceramic. The semiconductor fuse construction is given below.
The semiconductor fuse is also called current limiting or high breaking capacity fuse. The semiconductor fuses are sometimes referred to as rectifiers or ultra-fast fuses. The semiconductor fuse characteristics are given below.
The time taken by the fuse element for its melting is known as prearcing time.
The fuse element of the semiconductor fuse is made of oxidant-resistant fine silver with a melting point of 960°C, which can withstand the high operating temperature of the limiter. The fuse body is made of thermally stable aluminum oxide ceramic. The semiconductor fuse construction is given below.
Application of Semiconductor Fuse:
Semiconductor fuses are widely used for the protection of power semiconductor devices. The semiconductor fuses are used in the following equipment.
- DC Drives
- AC Drives
- UPS system
- Soft starter
- Electronic equipment
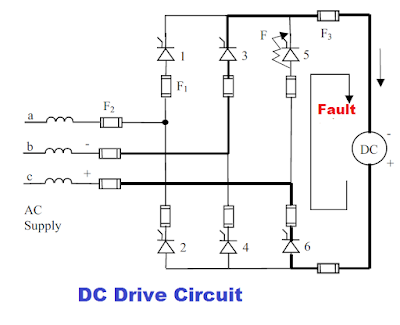
The Semiconductor fuses are also used in soft starters.
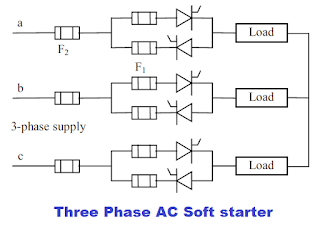
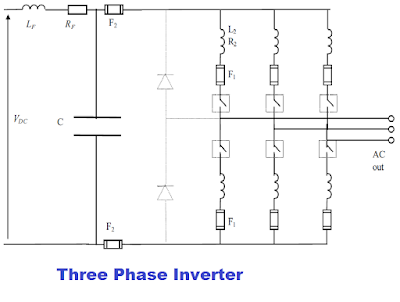
The semiconductor fuses are used for the inverter with IGBTs, thyristors, or Power transistors.
Thanks for such a insightful information about semiconductor fuse, It means a lot.