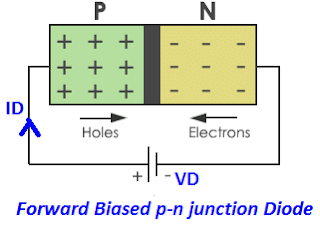
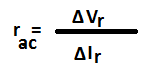The property of the material that offers opposition to the flow of electrons or electric current is known as resistance. A p-n junction diode allows current when it is forward-biased and blocks the current when it is reverse-biased. However, the diode does not allow the current to be completely under forward bias and does not block the current in reverse bias. Ideally, the diode must have zero resistance in forward biasing and infinite resistance in reverse biasing.
The depletion layer in the p-n junction diode offers resistance to the flow of electrons. The resistance offered by the diode under forward bias depends on the width of the depletion layer. When forward bias is applied, the width of the depletion layer decreases. However, the depletion layer can’t be completely eradicated. The thin layer of the depletion layer always exists. The resistance offered by this thin layer of depletion region under a forward-biased state is called the forward resistance of the diode.
When the p-n junction diode is reverse-biased, the width of the depletion region increases, and the charge carriers are blocked by the depletion layer. The resistance of the depletion layer is large because of its width. Under reverse biasing, the diode offers a very large resistance to the electric current. This resistance is called the reverse resistance.
In reverse bias, only a small amount of electric current due to a minority carrier flows through the diode. Thus, the resistance of the diode must be infinite in reverse bias, but, practically, it does not have infinite resistance because of the current flowing through the depletion layer due to minority charge carriers.
There are two types of resistance of the p-n junction diode.
1. Forward Resistance of diode
2. Reverse Resistance of diode
Forward Resistance of Diode
The resistance of the forward-biased diode is called forward diode resistance. The forward resistance can be further grouped into two categories.
1. Static Resistance or DC resistance
2. Dynamic Resistance or AC resistance
Static Resistance or DC Forward Resistance of Diode
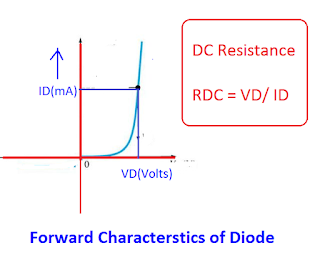
When DC is fed to the diode, the current flows in one direction. The resistance offered by the diode is called the DC resistance.
Formula of Forward DC Resistance of Diode
| RDC = VD / ID |
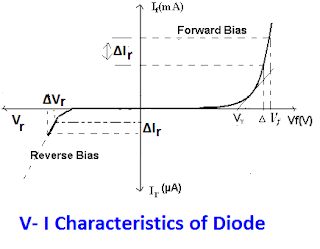
V- I characteristics of the forward-biased diode are given below.
Solved Example on Forward Resistance of diode
Calculate the DC resistance of the diode of the following V-I curve.
a) ID = 2 mA
b) ID = 20 mA
c) VD = -10 Volts
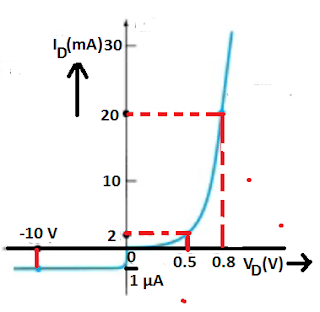
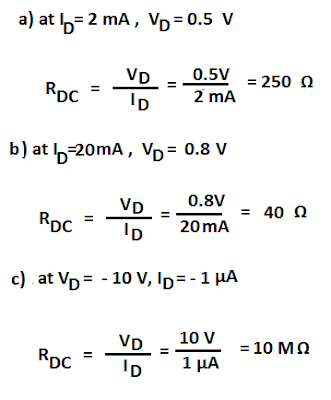
The forward resistance of the diode decreases with an increase in the forward biasing voltage.
Dynamic Resistance or AC Forward Resistance of Diode
The resistance offered by the diode when AC is applied to the diode is called AC resistance or dynamic resistance. The current flows in both directions when AC voltage is applied.

The V-I curve of the p-n junction diode is as given below.

The ratio of change in voltage to change in current represents the dynamic resistance of the diode. It is denoted by rac.
Formula of AC resistance or Dynamic Resistance of Diode
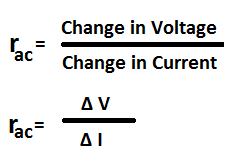
Reverse Resistance of Diode
When a reverse bias is applied to the p-n junction diode, the width of the depletion layer increases, and it offers higher resistance to the flow of charge carriers.
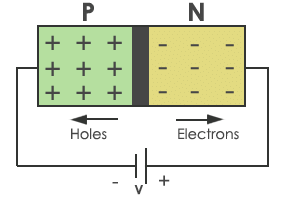
The reverse resistance of the p-n diode is in order of mega ohms. The reverse resistance is very large compared to the forward resistance of the diode.
The static reverse resistance of the diode can be calculated by following mathematical expressions.
Formula of Reverse DC Resistance of Diode

The dynamic reverse resistance of the diode is as follows.
Formula of Reverse Dynamic Resistance of Diode