In atomic and nuclear physics, the electron Volt or eV is used as a unit of energy. Joule is also a unit of energy, but it is a very large unit while dealing with electrons in atomic and nuclear physics.
The eV energy unit shows the energy of smaller particles like electrons.
Derivation of electron Volt(eV)
When voltage is applied to an electric circuit, current starts flowing according to the circuit’s resistance or impedance. Let the voltage applied be V and the current flowing in the circuit be I.
The power drawn by the circuit is;

The current in the circuit is equal to the rate of transferring the q charges from the lower to the higher potential point.

Putting the value of equation(2) in equation(1), we get

The energy is the capacity to do work. The energy is the power integrated over time.

Putting the value of power Equation(3) in Equation (4), we get

Therefore,

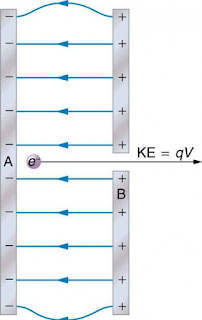
The charge Q coulomb travels against an electric field of voltage V, then the work done by the charge is – QV.
If the electron crosses the electric field of 1 volt, the work done is equal to ;

Definition of electron Volt(eV)
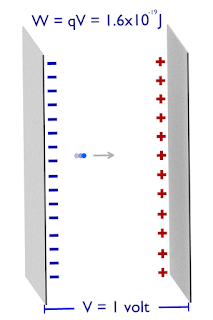
One electron volt is equal to the amount of work done in bringing the one electron against the electric field, having a potential difference equal to 1 volt.