Synchronous Speed
When three phases which are 120 degree-electrical apart are fed to the stator winding of the induction motor, a rotating magnetic field is produced which rotates in the space and time. The speed of the rotating magnetic field is called the synchronous speed of the motor. The synchronous speed is denoted as Ns. The synchronous speed can be expressed by the following mathematical expression.
Synchronous Speed Formula
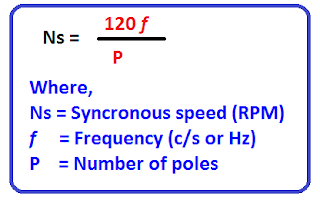
The synchronous speed of the motor depends on;
- Frequency of the supply source
- Number of poles of the motor
The synchronous speed of the motor remains constant if the number of poles and the frequency are constant. However, the synchronous speed can be changed by changing the number of poles or the frequency. A machine that runs at a synchronous speed is called a synchronous machine.
The synchronous speed of the motor with different numbers of poles is given below.
| No. of Poles | Frequency (50 Hz) | Frequency(60 Hz) |
| 2 | 3000 | 3600 |
| 4 | 1500 | 1800 |
| 6 | 1000 | 1200 |
| 8 | 750 | 900 |
| 10 | 600 | 720 |
| 12 | 500 | 600 |
| 16 | 375 | 450 |
| 20 | 300 | 360 |
Relationship between Speed and Frequency
The frequency of the emf generated in the stator depends on the frequency at which poles are rotating. In one complete cycle of the voltage generated, a pair of field poles passes over the coil.
Let the speed of the rotating magnetic field be N revolutions per minute(RPM).
n = N/60 revolution per second
Revolution/rotation per second = f
In one complete cycle, one pole pair passes over the coil. Therefore, the frequency of one pole pair passing is N/60. In one complete cycle, P/2 poles pass over a coil.
Number of poles in a complete cycle

The frequency of the poles passing in a one-cycle

Hence, for P poles, the frequency is;


Related Articles:
4 thoughts on “What is Synchronous speed? Relationship between speed and Frequency”